Payroll
How to Enable Electronic Regulatory Consent
1. Go to the Employee Essential page and select Employee Dashboard.
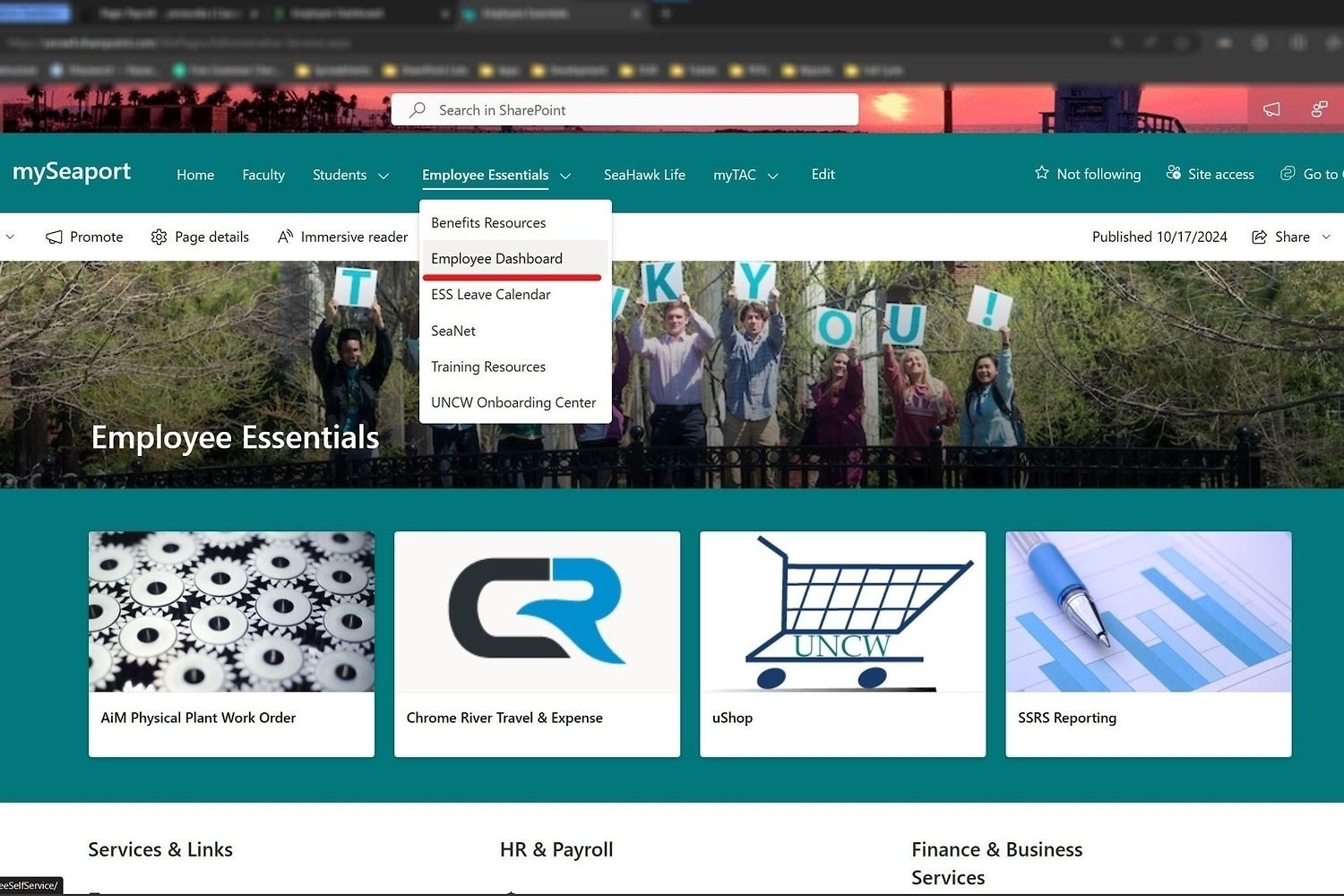

2. In Employee Dashboard you will see a section that lists several payroll options, select Taxes.
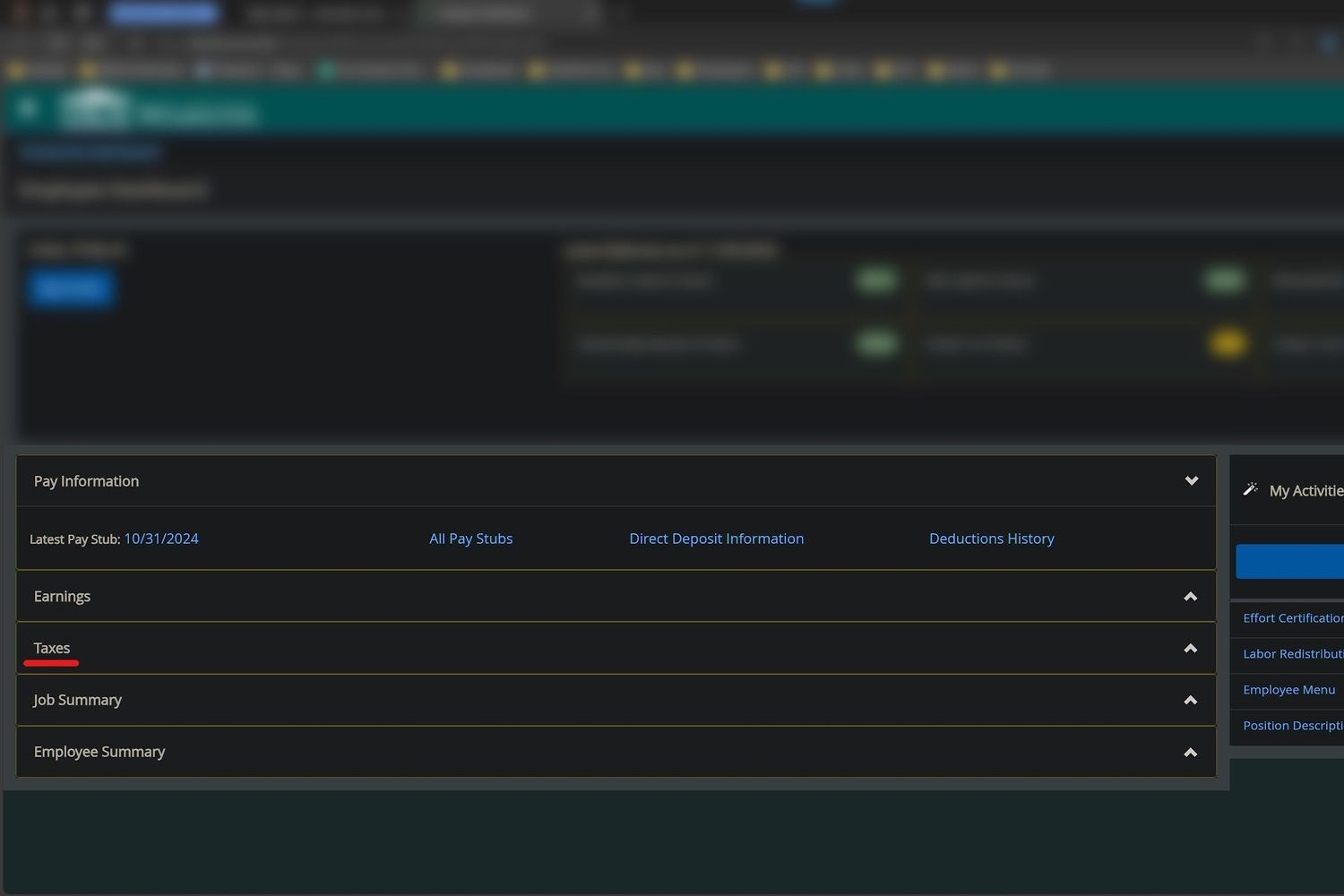

3. Select Electronic Regulatory Consent.
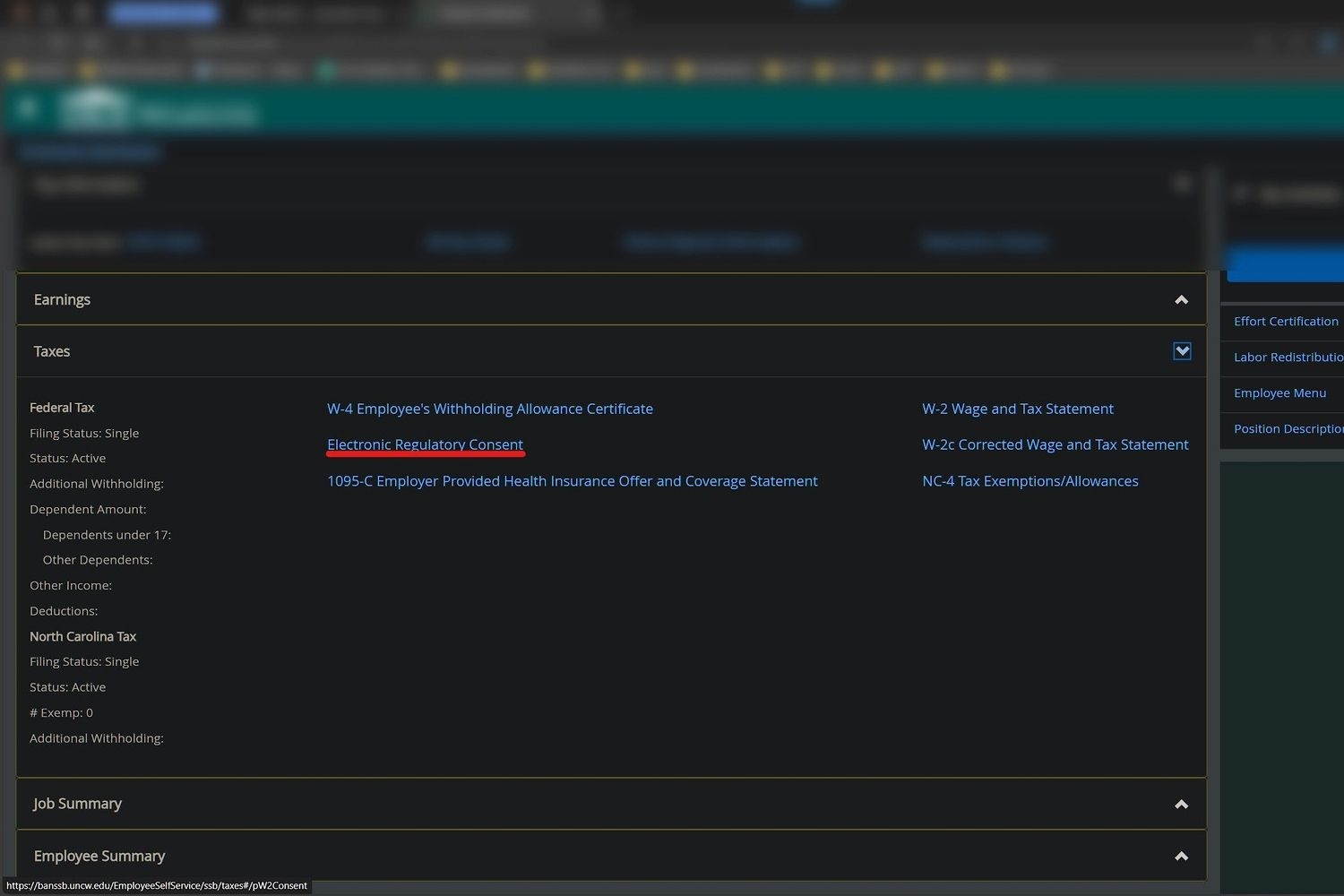

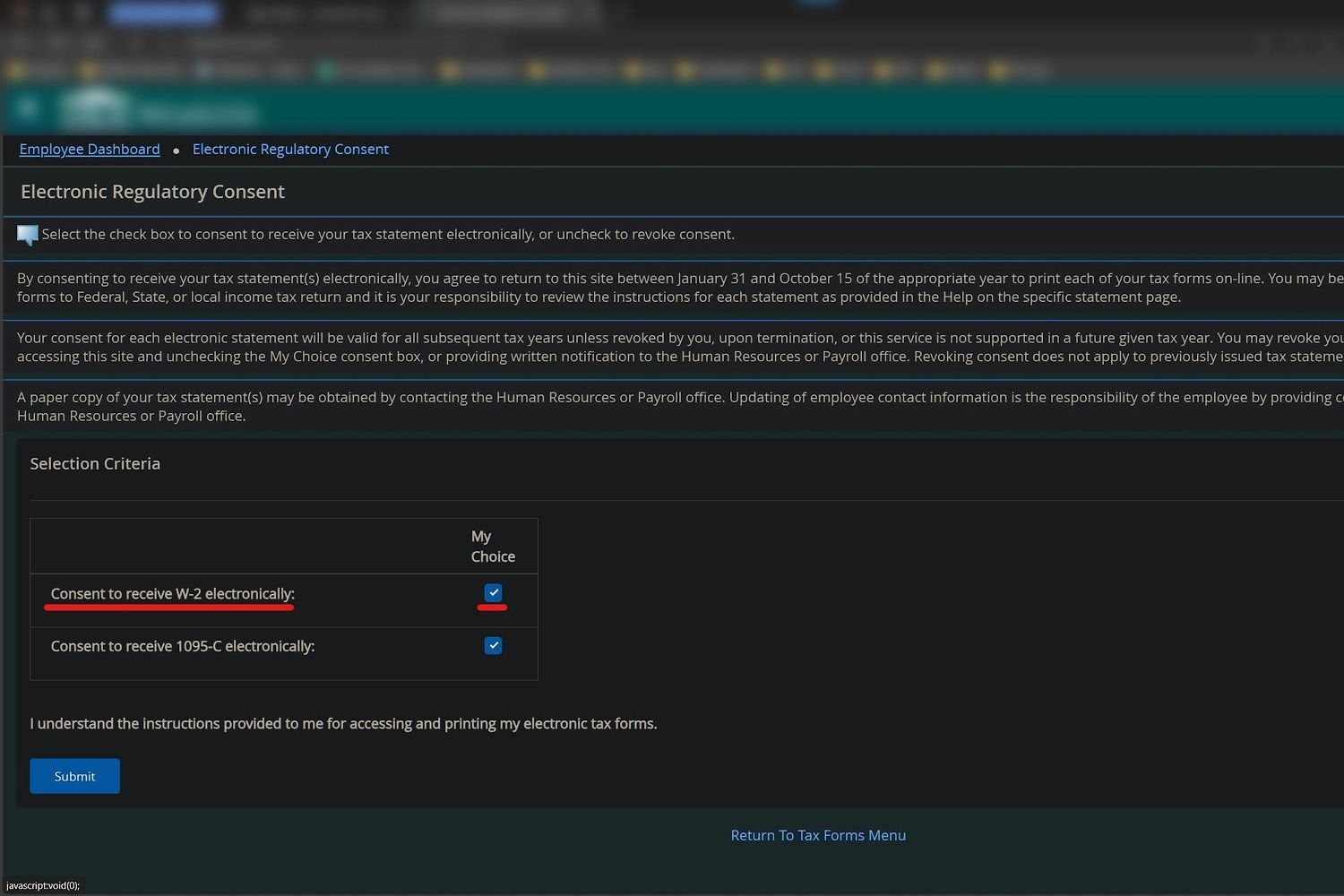
4. On the Electronic Regulatory Consent page check the box and click submit. Now you don’t have to wait on the mail or worry that your W2 is lost.

Contact Us
Please call or email first.
We are located on the second floor of the Administrative Annex on MacMillan Drive.
